KAIST
BREAKTHROUGHS
Research Webzine of the KAIST College of Engineering since 2014
Fall 2025 Vol. 25Satellite-based monitoring technique for urban ground deformation and geohazards
Satellite-based monitoring technique for urban ground deformation and geohazards
A satellite-based geohazard monitoring technique based on Sentinel-1 Permanent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (S1-PSInSAR) analysis is successfully developed and implemented for long-term monitoring of ground deformations in urban reclaimed lands.
Article | Spring 2023
With recent climate changes and rapid urbanization, natural and man-made geohazards associated with ground deformation poses a risk to the resilient urban environment, jeopardizing functions of infrastructures, buildings, and facilities and threatening human lives. Therefore, societal demands in systematic monitoring of ground surface deformation grows rapidly to minimize geohazard risks. With increasing availability of publicly shared satellite remote sensing data, a challenge has garnered much attention from engineers if those pseudo real-time satellite-based remote sensing data can be used for ground monitoring and geohazard risk management.
The research team, led by Professor Tae-Hyuk Kwon with his Ph.D. candidate, Ryan Ramirez of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, has demonstrated the feasibility of using the space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data from Sentinel-1 mission for long-term monitoring of ground surface deformations over reclaimed lands in Korea. Specifically, the team exploited a Permanent Scatterer Interferometric SAR (PSInSAR) analysis technique and remote sensing data from Sentinel-1 (S1) mission. The SAR data are publicly shared and includes regional scale coverage and a medium ground resolution, acquired day and night under any weather condition. The technology analyzes the phase stability of ground objects or PS using tens to hundreds of SAR acquisitions.
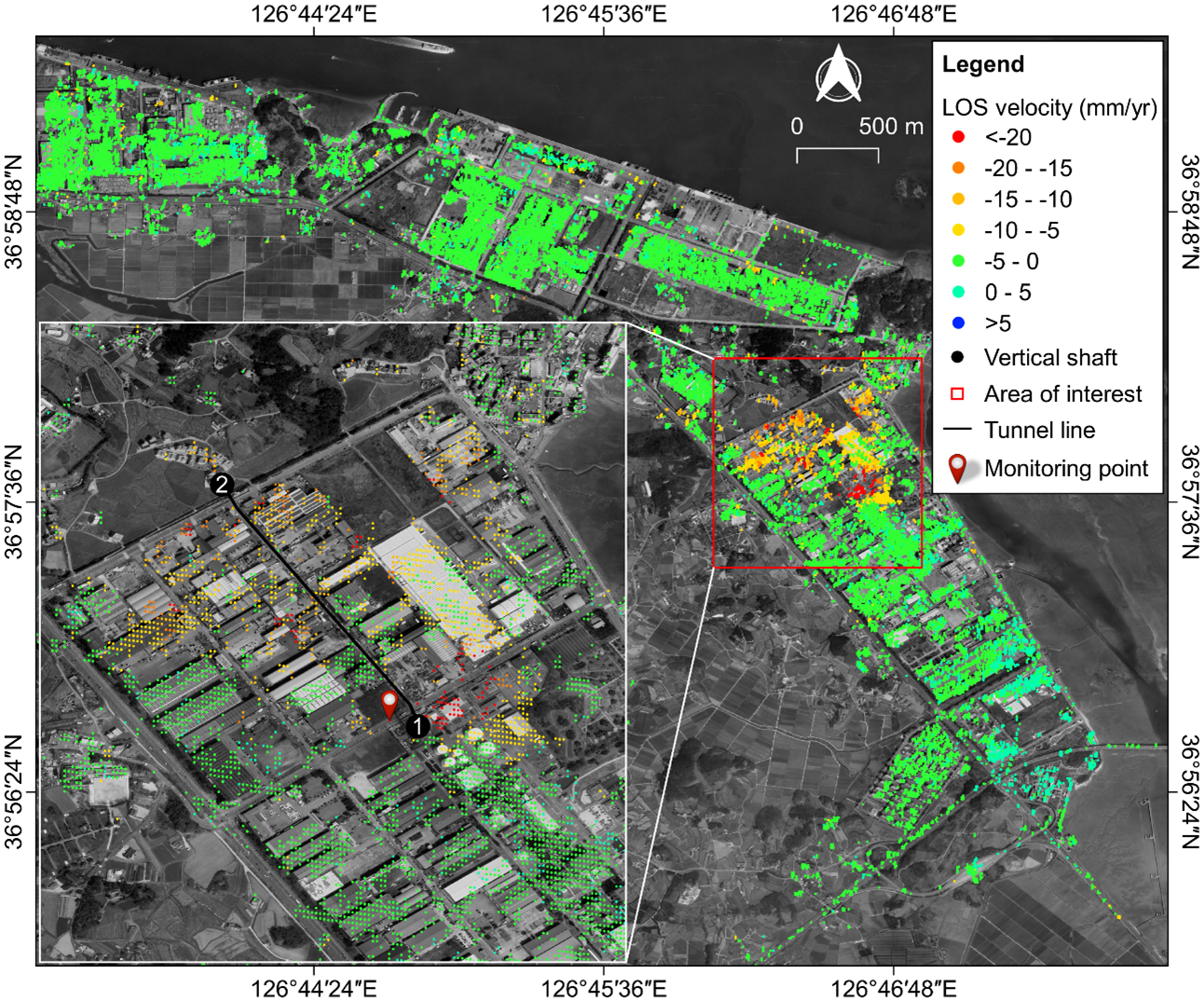
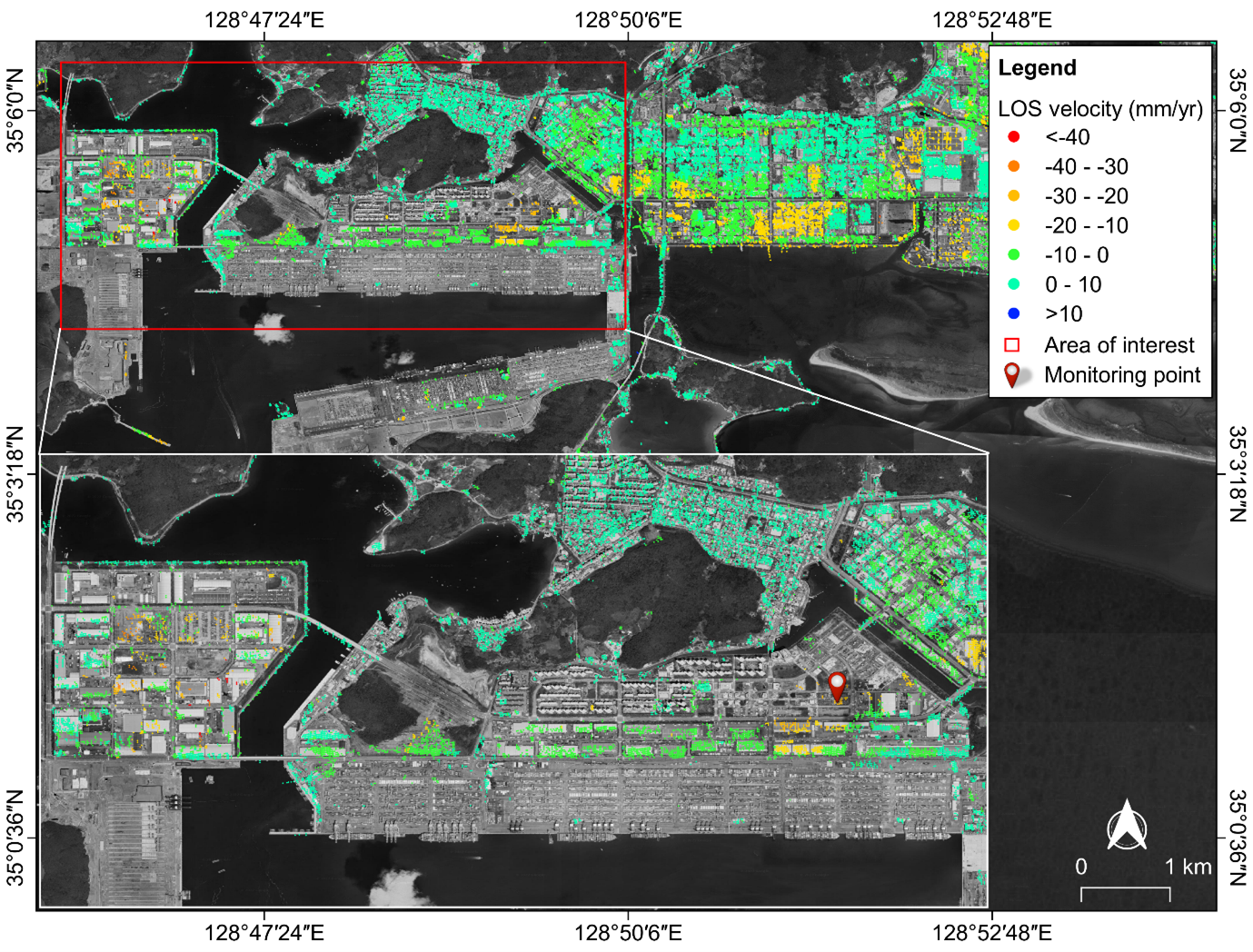
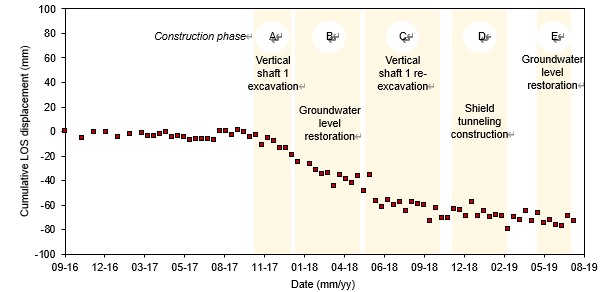
The S1-PSInSAR technology was successfully applied in detecting and monitoring excessive nonhomogeneous and nonlinear ground surface deformation in two sites in South Korea: Bugok Industrial Complex in Dangjin (Figure 1) and Busan New Port in Busan (Figure 2). The S1-PSInSAR results described the spatio-temporal evolution of ground surface deformation in the Bugok industrial complex, which coincided with the ongoing tunnel construction activities (Figure 3). In particular, the S1-PSInSAR results were validated using precise leveling data and showed excellent agreement. Moreover, the team also applied the technology to investigate the massive ground collapse incident at Busan New Port in Busan, South Korea. The team fact-checked the ground surface deformation derived from the technology using news media reports and historical archived research articles. The geological and geotechnical data acquired for the two reclaimed land sites also supported the estimated ground surface deformations. The S1-PSInSAR technology provides a cost-efficient non-intrusive tool for long-term remote monitoring of ground surface deformations endangering critical structural and geotechnical assets.
The research outcomes were published in the International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2022.102721) in April 2022 and in the KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering (https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-1005-5) in August 2022.
Relevant References:
Ramirez, R.A., Lee, G.J., Choi, S.K., Kwon, T.H., Kim, Y.C., Ryu, H.H., Kim, S., Bae, B., and Hyun, C. (2022) “Monitoring of construction-induced urban ground deformations using Sentinel-1 PS-InSAR: The case study of tunneling in Dangjin, Korea”, International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 108, 102721. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2022.102721
Ramirez, R.A., and Kwon, T.H. (2022) “Sentinel-1 persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar (PS-InSAR) for long-term remote monitoring of ground subsidence: A case study of a port in Busan, South Korea”, KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 26, 4317-4329. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-1005-5
Most Popular

A New solution enabling soft growing robots to perform a variety of tasks in confined spaces
Read more
Towards a more reliable evaluation system than humans - BiGGen-Bench
Read more
Development of a compact high-resolution spectrometer using a double-layer disordered metasurface
Read more
AI-Designed carbon nanolattice: Feather-light, steel-strong
Read more
Dual‑Mode neuransistor for on‑chip liquid‑state computing
Read more