KAIST
BREAKTHROUGHS
Research Webzine of the KAIST College of Engineering since 2014
Spring 2025 Vol. 24The Department of Knowledge Service Engineering introduces a new social learning system that creatively leverages collective intelligence
The Department of Knowledge Service Engineering introduces a new social learning system that creatively leverages collective intelligence
We Study, a social learning system that creatively leverages collective intelligence, is near completion and ready for use by KAIST students.
Article | Spring 2014
IEEE Computer Society, one of the largest professional associations in the area of Information Technology, announced that “Supporting New Learning Styles” is a crucial trend in 2014. Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) platforms such as Coursera and edX have continued to build an active learning environment with an increasing number of lectures accessible from anywhere and have been used by an increasing number of users.
Moreover, collaborative web services (e.g., blogs and Wikipedia) support the creation of various user-uploaded learning materials, producing a vast amount of new lectures and learning materials every day. While providing a large number of learning materials is necessary to accommodate diverse learners’ interests and choices, it can also cause confusion and frustration as learners are overwhelmed by the sheer number of resources when they look for personally relevant materials.
Also, maintaining the initial momentum of a learner over time has been a serious challenge for any e-learning system as learning activities are mostly limited to the interactions with the system. WeStudy(http://westudy.kaist.ac.kr), a social learning system developed by a number of professors and students in the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering and several researchers in the KI-Knowledge Convergence Team, is an innovative e-learning system designed to overcome these common weaknesses of e-learning systems.
WeStudy is a key outcome of a project funded by the Korean Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning. The project, led by Prof. Wan Chul Yoon, is in its last phase (fourth year), and the developed system is being rigorously tested before its public release. The system exploits the power of collective intelligence by enabling each participating user to share useful educational resources (in the form of PDFs, PPTs, DOCs, webpages, audio/video clips, etc.) that they have found on the Web with other learners. Furthermore, it allows users to search learning materials using two complementary and tightly linked search views (list view and graph view), using not only keywords but also ratings and difficulty levels. In a recent user study, the graph search view was favored by more intuition-based decision style learners while the list search view was favored by the rest.
In addition, the system allows users to form virtual teams of their choice, ask questions to each other about learning materials, receive feedback from others for the materials posted, and find related learning materials through system-generated recommendations, among many other interesting functionalities. Thus, the system facilitates interactions between its users and active participation through material posting, feedback, and Q&A.
WeStudy suggests a major alternative approach to conventional lecturing and one-directional tutoring. The system is designed to unleash the dormant energy and the social dynamic potential of learners to enable constructive interactions among them, which in turn allows each learner to continue his/her study with sustained self-efficacy and heightened engagement. Such a model is expected lead the way in educational reform that is inevitable with the new technological and educational theoretical advancements. The system also supports personal learning management and user interaction based on multimodal user interfaces.
Underlying the attractive surface, the system rests on many innovative ideas, such as virtual peer groups, study caravans, and creative team interaction. Virtual peer groups are automatically formed based on learners’ similar characteristics. The similarities between learning dispositions of users are calculated by considering three main properties: prior knowledge, the learning goal, and the learning activity. Based on his or her virtual peer group, each user receives recommended information such as recommended learning materials that are most frequently viewed by the user’s virtual peer group. Unlike virtual peer groups, study caravans can support learning activities based on learners’ designated interests, not their learning history. When learners who have a common learning goal can build a team, creative team interaction supports discussions and knowledge creation in the team.
This system can be applied to Education 3.0, a new education system promoted in KAIST, or other educational institutions. In addition, a key technology in the system, such as creating virtual peer groups and study caravans, which have been patented for their originality, can practically be used in any area of e-learning, knowledge management, and information searching.
by Professor Mun Yong Yi (Department of Knowledge Service Engineering)
Most Popular

When and why do graph neural networks become powerful?
Read more
Smart Warnings: LLM-enabled personalized driver assistance
Read more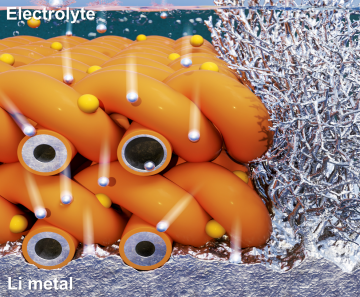
Extending the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries with water
Read more
Professor Ki-Uk Kyung’s research team develops soft shape-morphing actuator capable of rapid 3D transformations
Read more
Oxynizer: Non-electric oxygen generator for developing countries
Read more
