KAIST
BREAKTHROUGHS
Research Webzine of the KAIST College of Engineering since 2014
Spring 2025 Vol. 24Solar rechargeable wearable batteries
Lithium ion batteries are now being rebuilt to power conductive textiles and are being integrated with flexible solar cells in order to serve as power sources of wearable IT devices and, thus, accelerate the new era of consumer electronics.
Article | Fall 2014
IT technology is currently entering a new era of wearable electronics. Wearable electronics means that devices can be carried over clothes, glasses, and even human skin, eliminating the need to carry devices separately, representing a significant paradigm shift in consumer electronics. While other components, including circuits, sensors, and displays, have made substantial progress in this direction, the power source of the entire system, namely the lithium ion battery, has not kept pace with the ongoing trend, remaining as a hurdle for the entire technology. Lithium ion batteries still have the classical shapes of the rigid prismatic or cylindrical forms.
Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s group in the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability) at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has come up with the idea of using textiles as a battery current collector to overcome the limited physical motions of conventional lithium ion batteries. To give conductivity to textiles, his group has adopted the conventional electroless deposition process to coat the textiles with Ni or other metals. This simple modification of one key component in the cell allows for great tolerance against aggressive mechanical motions, such as bending and folding, without sacrificing the battery performance.
Choi’s group has proceeded one step further by integrating the wearable battery with flexible solar cells through collaboration with Prof. Jung-Yong Lee in the same department. The integration of solar cells allows for simple and comfortable recharging of the wearable battery without disassembly of the battery for each recharge. Furthermore, this textile-based concept has been expanded to a larger scale targeting a wider range of items such as outdoor tents, building roller blinds, and rollable displays. The demonstrated technology is currently being investigated further for scale-up with a domestic industrial partner.
The given work was published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A (2014, 2, 10862-10868) and Nano Letters (2013, 13 (11), pp 5753–5761) and was highlighted in Nature. In addition, the solar-battery integrated technology was selected as one of the top 10 power management technologies by EE Times Europe.
Additional links for more information:
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2014/TA/C4TA00551A#!divAbstract
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl403860k
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v504/n7480/full/504335e.html
Most Popular

When and why do graph neural networks become powerful?
Read more
Smart Warnings: LLM-enabled personalized driver assistance
Read more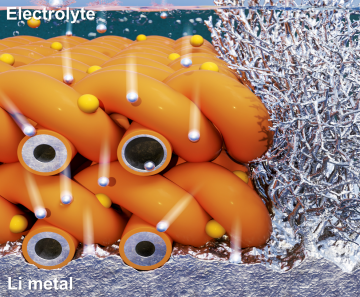
Extending the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries with water
Read more
Professor Ki-Uk Kyung’s research team develops soft shape-morphing actuator capable of rapid 3D transformations
Read more
Oxynizer: Non-electric oxygen generator for developing countries
Read more
