KAIST
BREAKTHROUGHS
Research Webzine of the KAIST College of Engineering since 2014
Spring 2025 Vol. 24How can the productivity of various manufacturing systems be improved efficiently?
How can the productivity of various manufacturing systems be improved efficiently?
Solution approaches based on a Petri net have been developed to address many scheduling problems of manufacturing systems with different objectives and constraints.
Article | Special Issue
The Fourth Industrial Revolution has enabled machines, robots, and jobs in factories to share real-time information and use it to increase the productivity and quality of production. Hence, obtaining an efficient production schedule in such a new production environment is becoming increasingly important and challenging. A scheduling problem of a manufacturing system is to determine a sequence of jobs and their starting times on the system to minimize total cost. The manufacturing systems for semiconductors, LCDs, steel, and automobiles have various configurations and require complex scheduling constraints, such as time window constraints to improve product quality, strict due dates of customer orders, material-handling systems transporting jobs, and diverse job flows. However, it is required to develop a new solution approach whenever a scheduling problem even with a slightly different constraint or objective is handled, which is time-consuming.
A research team led by Prof. Hyun-Jung Kim in the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has developed efficient solution approaches based on a Petri net, which is a graphical and mathematical modeling tool for discrete event dynamic systems. Most scheduling problems of manufacturing systems can be well modeled with a Petri net, and the proposed solution approaches based on a Petri net are then applied to those scheduling problems without large modification. Also, the real-time dynamic evolution of systems can be monitored with the Petri net.
A mixed-integer programming model and a branch and bound algorithm for obtaining an optimal solution of noncyclic scheduling problems have been developed based on a Petri net with fundamental mathematical properties and theories (Figure 1). They have also been applied efficiently to automated manufacturing systems that consist of material handling systems and multiple machines even with diverse job flows and time window constraints. Also, a reinforcement learning approach has been successfully applied to a Petri net for scheduling of robotic cells and provided competitive solutions compared to other well-known methods used in practice (Figure 2).
It is expected that this approach for solving complex scheduling problems with a Petri net can respond effectively to dynamically changing manufacturing environments. The research team of Prof. Hyun-Jung Kim is planning to develop advanced solution approaches based on a Petri net and to apply them to other complex scheduling problems.
Most Popular

When and why do graph neural networks become powerful?
Read more
Smart Warnings: LLM-enabled personalized driver assistance
Read more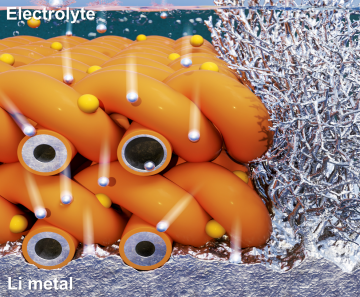
Extending the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries with water
Read more
Professor Ki-Uk Kyung’s research team develops soft shape-morphing actuator capable of rapid 3D transformations
Read more
Oxynizer: Non-electric oxygen generator for developing countries
Read more

