KAIST
BREAKTHROUGHS
Research Webzine of the KAIST College of Engineering since 2014
Spring 2024 Vol. 22Metaverse-based testbed developed for virtual autonomous vehicles

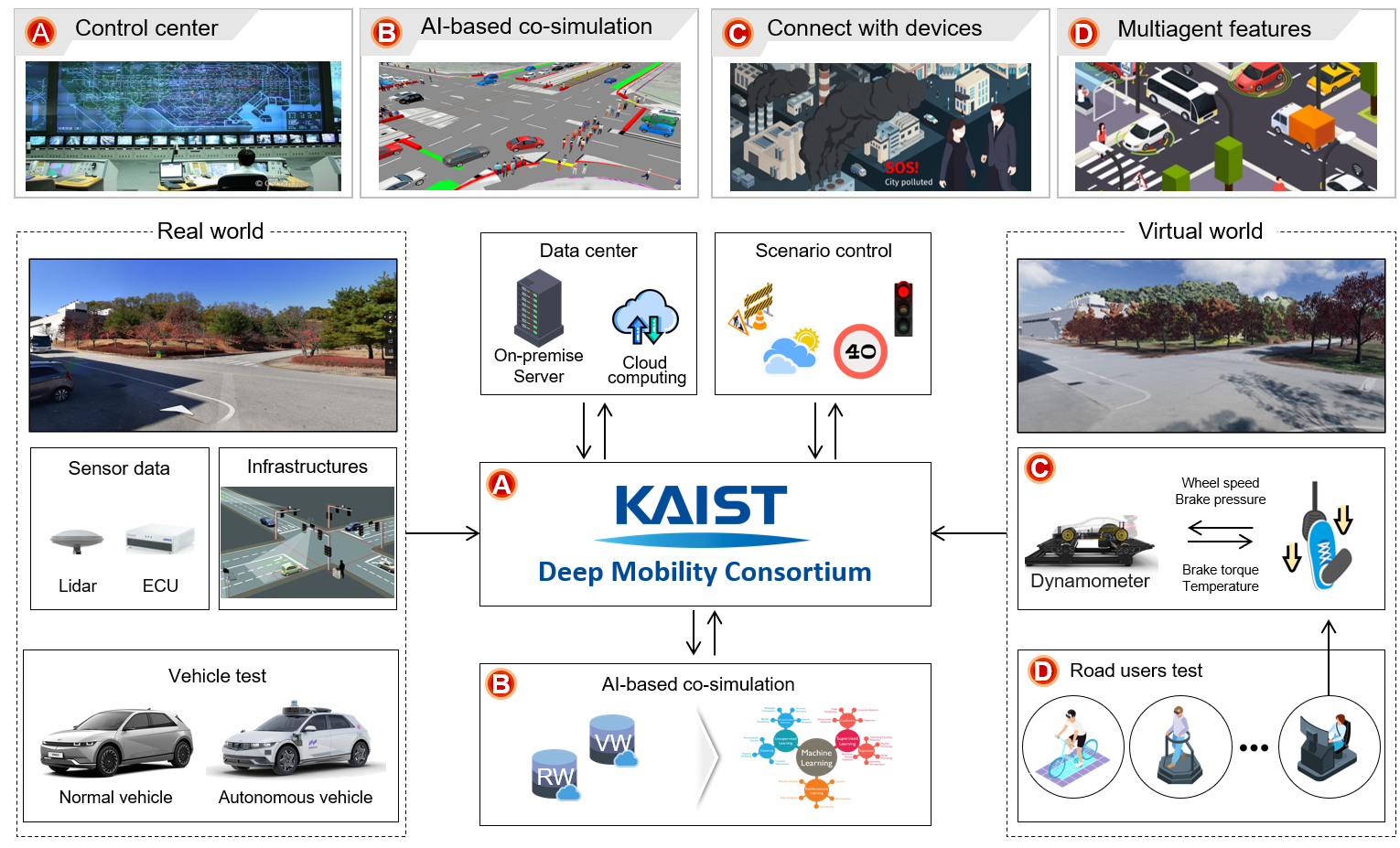
A Metaverse-based virtual testbed is used to test autonomous driving vehicles under various scenarios, which may be dangerous and costly in real life. In addition to serving a practical purpose, this virtual testbed strengthens the connection between vehicles, infrastructure, and services, which are the main entities of smart mobility.
Cho Chun Sik Graduate School of Mobility at KAIST established the KAIST Munji Campus as a metaverse-based virtual testbed for testing autonomous driving vehicles in a new dimension. There are many hurdles for autonomous driving technology to be operational in the real world. This is because vehicles must drive without accidents in any occasion in the real world. The existing tests are insufficient in alleviating concerns regarding the effectiveness of algorithms and the time, cost, and safety in testing due to limited assets.
To tackle this limitation, a metaverse-based virtual testbed based on KAIST Munji Campus was developed. This virtual testbed space is capable of (1) implementing realistic objects based on image and point cloud data using drone operation, (2) up to 20 players simultaneously accessing the metaverse environment to observe interactions among road users, (3) providing network communication between real-virtual objects through traffic infrastructure and vehicles, and (4) deploying naturalistic surrounding traffic flow by integrating with existing traffic simulations, such as Vissim or SUMO.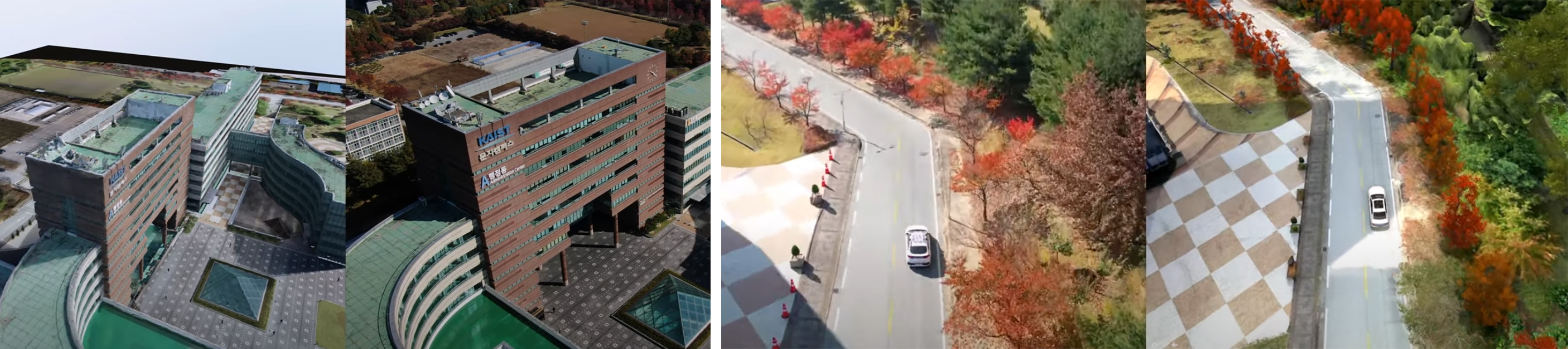

This testbed platform is being used as a part of the first academic-oriented consortium, called the KAIST Deep Mobility Consortium. The Deep Mobility Consortium, led by KAIST Professor Lee Dong-man, collaborates with professors and researchers in various fields to develop, maintain, and service various components defined as mobility, including varied means of movement, infrastructure, and transportation services on integrated mobility platforms.
In the future, the Cho Chun Sik Graduate School of Mobility plans to implement the learning and evaluation technology of autonomous driving algorithms, which has been almost impossible with the current existing technology, by incorporating real-world road users, infrastructure, AI, and cloud computing technology into the virtual world.
Most Popular
An intravenous needle that irreversibly softens upon insertion by body temperature
Read more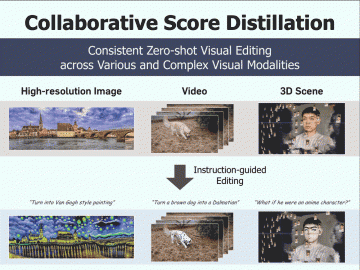
Consistent visual editing of complex visual modalities: videos and 3D scenes
Read more
SUPPORT enables accurate optical readout of voltage signals in neurons
Read more
AI for detecting aimbots in FPS games
Read more
Origami-based deployable space shelter
Read more